This tutorial which is part of our SAP FI course talks about SAP chart of accounts in Financial Accounting. You will learn what is a chart of accounts in SAP FI, their types, and how to assign them to company codes. We will mention the SAP transactions and tables that are relevant for this process.
In SAP, general ledger (G/L) accounts are created for an organization at the SAP Chart of Accounts level. SAP Chart of Accounts is a variant containing the definition of the structure and important information about G/L accounts. All the G/L accounts are splitted into multiple account groups, for example, assets, liabilities, expenses, income, etc. As per a company’s or business requirement, different account groups can be created at SAP chart of accounts level.
Master data of G/L accounts first needs to be created at the chart of accounts level and then it will be extended to a company code level(s). SAP chart of accounts is defined at the client level and needs to be assigned to company code or company codes.
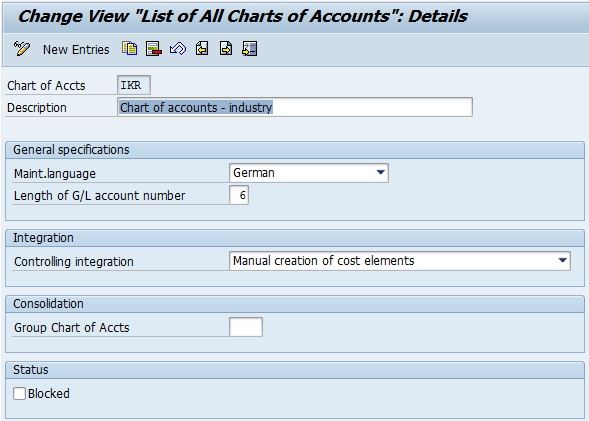
At the chart of accounts level we have to maintain a length of a G/L account and whether the cost element is to be created manually or automatically. In SAP S/4 HANA, a cost element will be maintained or defined at G/L account master data level. G/L account assignments are done at the SAP chart of accounts level for respective areas like FI-MM integration, FI-SD integration, FI-AA integration, etc.
Chart of Accounts Definition
Chart of account is a list of general ledger (G/L) accounts to be used by an organization or many organizations. It entails account number, description and field status(es) at the company code level.
Prerequisites
Before creating G/L account master data it is essential to maintain a retained earnings account at the chart of accounts level. It can be once or more than once. If the retained earnings account is one, then the SAP system considers it default one. In case if there are more than one retained earning accounts, while creating the G/L account master data user has to choose the relevant Profit and Loss (P&L) statement type.
For Profit and Loss G/L accounts it is obligatory to maintain a retained earnings account and at the time of year-end activities it will show the company’s financial results. All the P&L accounts balances are moved to retained earnings account while performing carry forward balances.
Account groups
The list of G/L accounts is separated into different account groups as per their nature. For example, expenses/assets. At the level of account group we define number ranges and maintain field statuses (like which field should be suppressed / required / optional in transactions) for G/L accounts. If necessary, we can limit the number of required fields to minimize input efforts of SAP business users.
Types of SAP Chart of Accounts
We have three types of chart of accounts in SAP as explained below.
Operational Chart of Accounts
Day to day business operations are booked in G/L accounts which created at the operational chart of accounts. These G/L accounts will be assigned in finance and controlling level. Assignment of the operational chart of accounts to a company code is mandatory.
Country Specific Chart of Accounts
G/L accounts in country specific charts of accounts are created to fulfill legal requirements of a particular country. It allows to provide reports and/or statements at the country level. Assignment of a country specific chart of accounts to a company code is optional.
Group Chart of Accounts
G/L accounts created under a group chart of accounts are used by the entire corporate group. This chart of accounts allows to provide information or reports at the corporate level or all the company codes of an organization. These G/L accounts are used for consolidation purposes and assignment of a group chart of accounts to a company code is optional.
Assignment of SAP Chart of Accounts to a Company Code
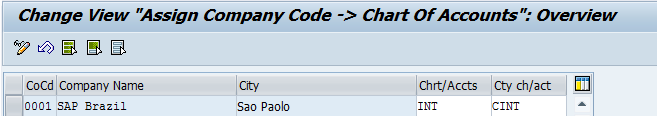
To create G/L account master data at the company code level it is vital to assign an operating chart of accounts to a company code. One chart of accounts can be assigned to multiple company codes. Assignment of a country specific chart of accounts to a company code is not mandatory. But according to the country requirements, it has to be assigned and defined. The configuration and setup is the same for an operational chart of accounts and a country specific of chart of accounts. G/L account master data won’t be extend at the company code level for country-specific chart of accounts.
Customizing Path: SPRO – SAP reference IMG - Financial Accounting (New) - Financial Accounting G/Lobal Settings (New) - Master Data - G/L Accounts – Preparations - Edit Chart of Accounts List/Assign Company Code to Chart of Accounts
Transactions: OB13/OB62
Relevant tables: T004 (Directory of Charts of Accounts), T001 (Company codes)
Screenshots
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP FI tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP G/L Account Segments
Go to previous lesson: SAP Exchange Rate Table
Go to overview of the course: Free SAP FI Training

Hi,
This is Good answer to begeneers
Regards
Madhu
Hi ,
do we need to create diff gl account type/range in country chart of accounts as compare to operating chart of accounts ? Can you provide an example what kind of transaction will need country chart of accounts and why it cant be done with operating chart of accounts.
What is the t-code to just view & print the chart of accounts for a specific company code?
FBL1N, select only the company code you wish to by filtering it