 In this SAP BASIS tutorial, we will discuss SAP Application Servers and their instances. You will learn about two main types of SAP Application Server instances and their architecture.
In this SAP BASIS tutorial, we will discuss SAP Application Servers and their instances. You will learn about two main types of SAP Application Server instances and their architecture.
An SAP Application Server instance defines a group of resources such as:
- Memory
- Work processes
- Dispatcher
- Gateway
- Internet Communication Manager
for a single application or database server in SAP system. When the SAP application instance and database instance reside on the same hardware, it is then known as a “Central System” setup. When the application instance and database instance do not share the same hardware resources, then the instance is known as a “Distributed System” setup.
An SAP Instance is uniquely identified with a SAP system ID, known as SID (System ID) and an instance number (2-digit number) from 00 to 99.
Example:
System ID: ERD
Instance No: 00
Each SAP instance can be distributed over multiple hardware units. These units can be a separate server or host, virtualize, logical or physical partitions within the same server or host. An instance is configured through an instance profile. An instance is also called application server in the software-oriented view of the client server model.
In an SAP NetWeaver application, it must have minimum one application server and can have multiple application server instances. The SAP application server instances process any incoming user requests. If there is more than one application server instances, there is one main instance that contains 3 core services which is the message server, the enqueue server and a start service.
This main instance we called it Central Instance (CI) or Primary Application Server (PAS) instance which consists of 3 core services and other services process like ABAP dispatcher, gateway and ICM.
For distributed system, the 3 core services are separate in one instance and we called it ABAP System Central Instance (ASCS). The ASCS instance is used to manage locks, exchange any message and perform load balancing in the SAP system. There is no dialog process in ASCS instance.
Architecture of SAP NetWeaver Application Server for ABAP (SAP AS ABAP) is shown below:
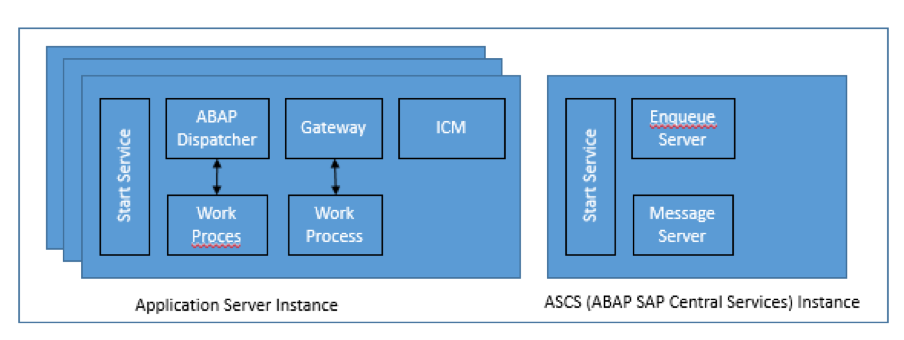
The working process for SAP AS ABAP is as follows:
Message Server (ABAP MS)
It handles communication between distributed dispatchers in SAP ABAP system. This process is configured only once for each SAP system. One of the vital services in SAP for SAP startup.
Enqueue Server (ES)
The lock table mechanism in the system manages by enqueue server components.
Gateway (GW)
It enables communication between two SAP system or between SAP system and external systems. It exists once per application server and can also be installed as standalone gateway.
Internet Communication Manager (ICM)
It allows communication with the SAP system using web protocols such as http, https or smtp. There is exactly one ICM process per SAP application server.
ABAP Dispatcher
Consist of SAP Work process. It separately executes individuals function in SAP applications such as Dialog, Update, Background Work process and Spool Work process.
SAP Central Instance (CI) / Primary Application Instance (PAS)
In Central System, SAP Central Instance is consisting of Message Server (MS), Gateway (GW), Internet Communication Manager(ICM) and Dispatcher Process (Disp) and one or more Enqueue (Enq) work process. Now, SAP has changed the terms of CI to Primary Application Server (PAS).
For Distributed System Setup, where Message Server and Enqueue process on separate instance which on (ASCS), Central Instance (CI) and Dialog Instance (DI), the different is only on SAP profiles while the process are the same.
In summary:
CI/PAS = MS + GW + Disp + Enq + ICM

SAP Dialog Instance (DI) / Additional Application Instance (AAS)
Dialog Instance (DI) is an additional application instance on top Central Instance (CI). Normally we will be setting up DI on a different host.
But Dialog instance is only consisting of Gateway (GW), Internet Communication Manager (ICM) and Dispatcher Process (Disp) only. There is no Message Server and Enqueue Work Process.
DI instance will always start after CI instances start because it will depend on CI instance as the main instance where message server and enqueue server exist. Normally we setting up Dialog Instance for load balancing and to handle more workload rather than only have Central Instance. The new name for DI is Additional Application Server (AAS).
In summary:
DI/AAS = GW + ICM + Disp
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP BASIS tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP ABAP and JAVA Stacks
Go to previous lesson: What is SAP NetWeaver?
Go to overview of the course: Free SAP BASIS Training

Superb ,very useful
Hello
What information do I need to submit as the logon information? And is there any special requirements in order to logon to a server?
hi sir,
i am thinking to start to learn sap basis .now i am getting confusion b/w sap mm and sap basis.
and i just want to know that do we have future in sap basis? hence the automation has been implemented in sap s/4 HANA.
so if i learn SAP BASIS now,if in future i might bein the jobless /need to learn other module situation?
SAP BASIS is not just a module. SAP BASIS is the implementation, integration, administration and maintenance of SAP Netweaver platform. Netweaver is called the Basis of SAP Platform that is why the word SAP BASIS came.