 Welcome to this familiarization tutorial on SAP Human Capital Management (HCM). The objective of this tutorial is to provide SAP HCM overview and discuss its components.
Welcome to this familiarization tutorial on SAP Human Capital Management (HCM). The objective of this tutorial is to provide SAP HCM overview and discuss its components.
SAP HCM is a comprehensive business solution to automate, streamline and optimize the various HR processes of a company, from recruit to retire. While HCM consists of many seamlessly integrated sub-modules, this tutorial will focus on some of the predominant ones as listed below.
Recruitment
The first component that we are going to discuss in SAP HCM overview is Recruitment. This component facilitates the end-to-end recruitment process of a company.
Key Features
- You can manage vacancies and advertisements, and assign vacancies to advertisements.
- Applicant administration enables the storage of all applicant data and classification of applicants.
- You can create letters for applicant correspondence, such as interview invites and offer letters.
- Selection of applicants is facilitated using applicant actions, such as “Invite applicant” or “Issue offer letter”.
- If an applicant is selected and you decide to hire him/her, the applicant data can be transferred to Personnel Administration. This eliminates the duplication of data entry effort.
- Various reports are provided to generate statistical data and lists on advertisements, vacancies and applicants.
Personnel Administration
Personnel administration is often considered the backbone of the SAP HCM module. And rightfully so. It is in this space that employees are hired, all their information is stored and their employment life cycle is recorded.
Key Features
- All employee data is stored in infotypes. Infotypes are logical groupings of related data fields. For example, an employee’s name, surname, birth date, marital status and religion are stored in the Personal Data infotype.
- Changes made to infotype data can be logged and subsequently analysed. You can control, via customizing, which infotypes and fields should be logged.
- Personnel actions are used to record personnel procedures like hiring, transfer, promotion and separation.
- HR authorizations ensure that all infotype data is secure and accessible to authorized users only.
- Several standard reports are provided to efficiently extract and evaluate HR data. If these do not meet the reporting needs of your company, ad hoc queries or customized reports can be developed.
Organizational Management
As we continue SAP HCM overview, let’s talk about organizational management for human resources in SAP ERP. This component is the basis for various business and HR processes, as well as for workflows. It is here where the organizational plan (a functional structure of an organization) is created and managed. The below picture shows an illustrative example of an organizational structure.
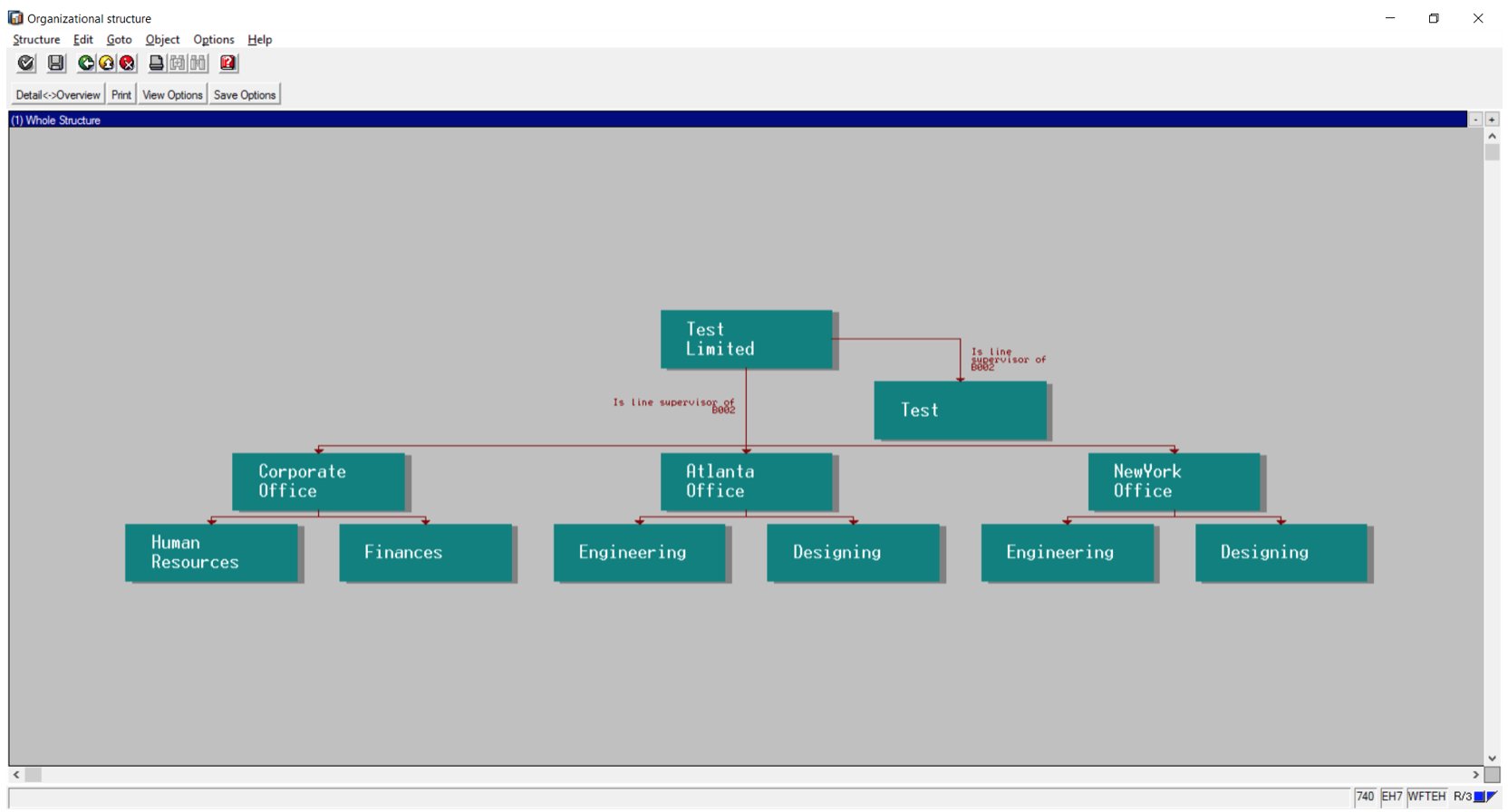
Key Features
- Organizational management is designed around the concept of objects, and relationships between the objects. There are numerous objects, the most important ones being Organizational Unit, Position, Job, Person and Cost Center.
- Objects are linked to each other via relationships. These relationships give rise to structures. For example, the relationships among organizational units (business units, departments, groups or teams) result in the organizational structure. The relationships between positions (e.g. the Assistant Manager position “Reports to” the Manager position) result in the reporting structure.
- These structures are of prime importance for the implementation of workflows.
- SAP provides various interfaces to efficiently create and edit objects, relationships and structures. Each of these interfaces will be covered in detail in the SAP HCM Organizational Management tutorial.
- Numerous reports are provided to efficiently extract and evaluate organizational data.
Time Management
Time management is the SAP HCM component that facilitates the planning, recording and valuation of employees’ working times.
Key Features
- Work schedules are used to indicate an employee’s planned working time, daily working hours, weekly work pattern and weekly days off. The below picture is an example of a work schedule:
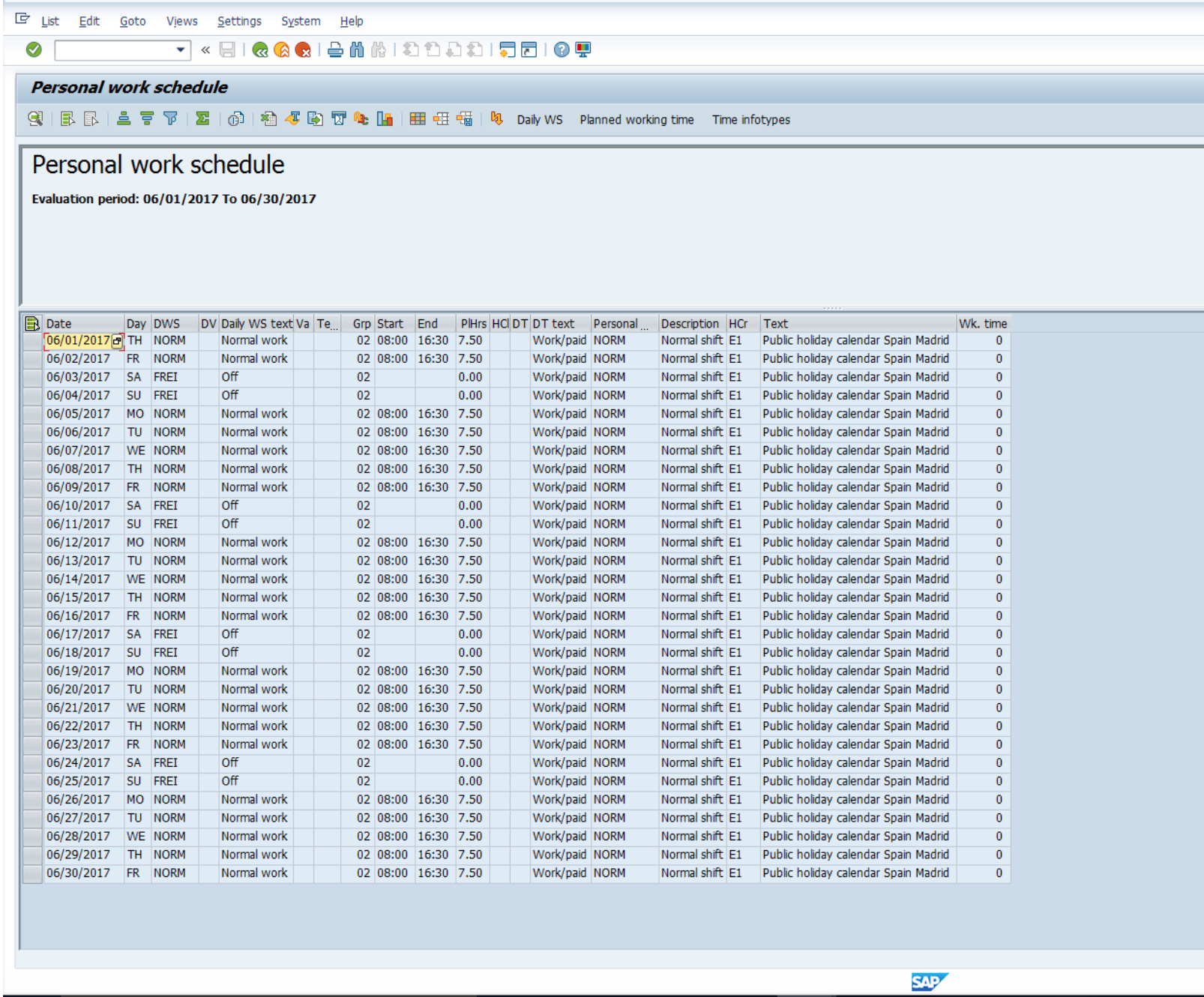
- Public holidays can be created and assigned to holiday calendars.
- Employee time data can be recorded by employees themselves or by time administrators, supervisors or secretaries.
- Quota generation can be used to calculate leave entitlement in accordance with your company’s leave quota policy.
- There are two types of time management:
- Positive Time Management – All actual times must be recorded. This implies that, for any day, an employee will be considered absent unless a clock-in and clock-out action is recorded for that day. Attendance may also be manually entered by a manager.
- Negative Time Management – Only deviations from the work schedule must be recorded. In this case, for any day, an employee will be considered present unless an absence is explicitly recorded for that day.
- Time Evaluation is an optional sub-component which can be used to evaluate employees’ working times.
- Time Management can be integrated with Payroll. The payroll driver reads the inputs from time management, for example, to compensate overtime hours or to calculate loss of pay.
Payroll
SAP provides a robust payroll solution to calculate gross earnings, deductions and net pay in accordance with legal as well as company-specific policies.
Key Features
- Statutory regulations of every country are incorporated in country-specific payroll drivers provided by SAP.
- Company-specific payroll policies can be implemented through customizing and with the help of personnel calculation rules.
- Payroll inputs are read from payroll-relevant infotypes. These are then processed by the payroll driver, various calculations are performed and the payroll results are written to cluster tables.
- Payslips, company-specific reports as well as statutory reports can be generated.
- In addition to regular payroll carried out at fixed intervals, payroll can be executed as needed using off-cycle payroll.
- The payroll results can be posted to Accounting.
Objective Setting and Appraisals
There are two dimensions to implementing this component:
- The designing of the appraisal template
- The mapping of the end-to-end appraisal process
Key Features
Appraisal template
- The company’s appraisal form can be mapped in the system by copying a reference template or by creating a new template from scratch.
- You can create as many templates as required.
- Appraisal documents for each appraisee are then created by first selecting the template.
Appraisal process
- The appraisal process specifies how the appraisal document should flow from one participant to another and what document status should be assigned at every phase.
- An end-to-end process consists of the below phases:
- The Objective Setting Phase, wherein concrete objectives are set for the employee and agreed upon between the employee and manager. Training and development needs are identified.
- The Review Phase, wherein the agreed upon objectives are revisited and adjusted if required.
- The Appraisal Phase, wherein the employee’s performance is assessed against the set objectives.
Training and Events Management
This SAP HCM component enables you to plan and manage your company’s training calendar and all booking-related activities.
Key Features
- Design a hierarchical training catalog comprising business event groups and business event types.
- Plan and create business events which represent actual courses and dates. See the illustration below, where objects with code L represent business event groups, objects with the code D represent business event types and objects with the code E represent business events:
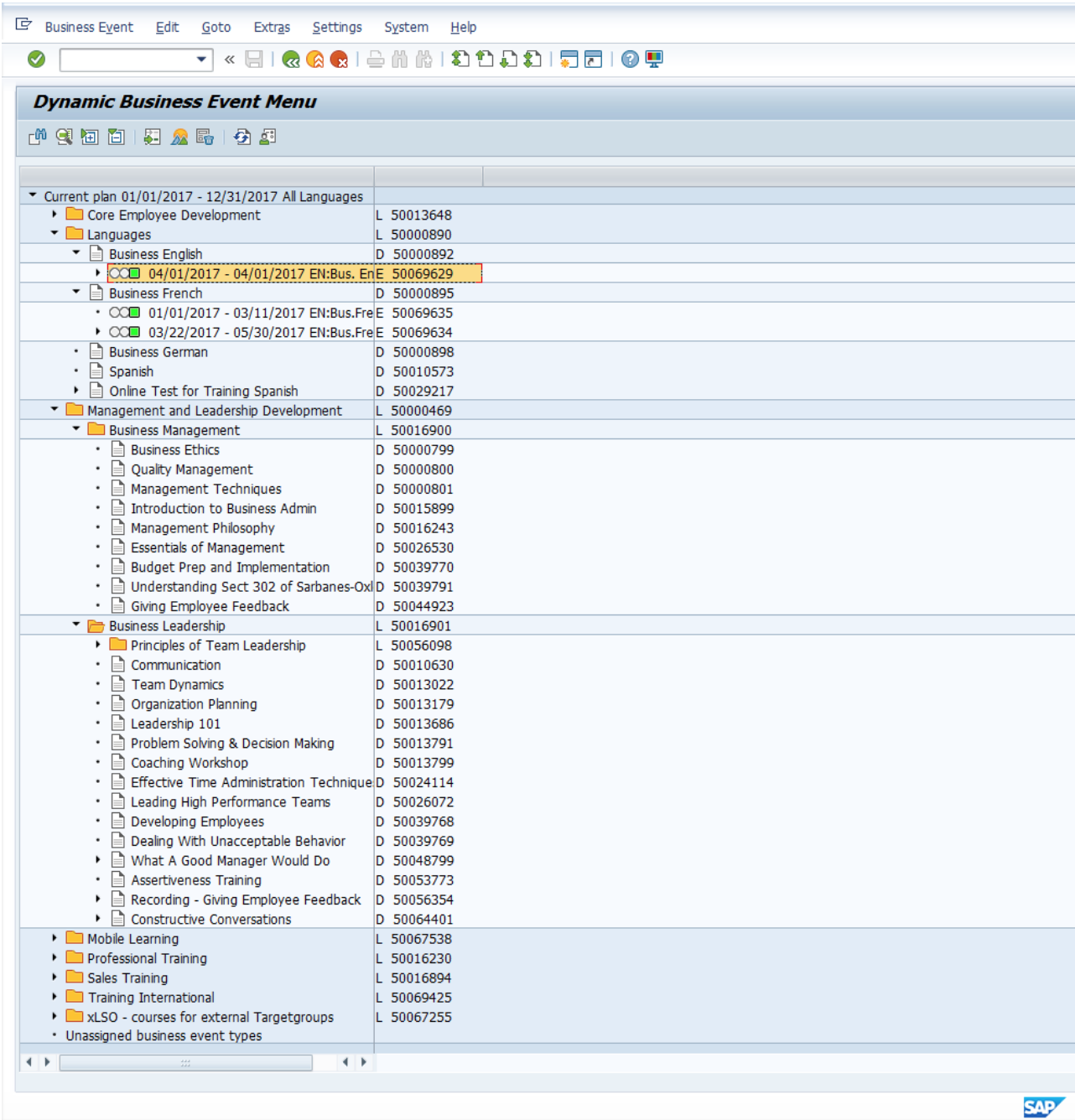
- Create and allocate resources such as room, instructor and material.
- Cancel a business event by specifying the cancellation reason.
- Carry out various functions like pre-booking an attendee to a business event type, booking an attendee to an event, re-booking, replacing an attendee and cancelling an attendance.
- Incorporate checks during bookings. For example, check that the attendee has the prerequisite qualifications to be eligible for the course.
- Output training correspondence automatically or manually.
- Transfer qualifications to an attendee on successful completion of a training program.
- Use comprehensive reports to extract data on business events and attendances.
Self-Services
The last but not the least sub-module of HCM solution that we are going to cover in this SAP HCM overview is self-services. SAP HCM self-services allow employees and managers to be directly involved in HR processes, thus reducing cycle time, eliminating red tape and ensuring better service.
Key Features
- Employee Self-Service (ESS) and Manager Self-Service (MSS) are portal-based solutions which are accessible via the Internet or the company’s intranet.
- ESS allows employees to create, view and edit their own data. Employees can also view their personal information, payslips, leave history, nomination details etc. Based on company policy, employees can edit data with or without approval. This has the dual benefit of empowering employees to keep their data updated, as well as reducing the workload of the HR team.
- MSS is a one-stop solution for managers to perform their tasks, approve work items and access important information about their subordinates.
- An employee can submit a leave request via ESS. This will be sent to the manager for approval via MSS. If approved, the leave will automatically be stored in SAP in the Absences infotype.
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP HR tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP HR Basics and Navigation
Go to previous lesson:
Go to overview of the course: SAP HR Training

This was very interesting since I do not currently see SAP directly but I would like to refresh my knowledge and why not certify myself
Iam employ of an government organisation how i can get more experties in hR
Try doing SAP CERTIFICATION from SIEMENS
This is very good and helpful.
Thankyou
Hi,
From where I can get a dummy SAP to practice my self.
Else how can I do practice my self in SAP HCM.
Thanks in advance,
Regards,
Hemant
I am a Human Resource Professional. I want to navigate through SAP HCM modules to understand what are its features and functionalities. Kindly guide for the same. Are there any online SAP HCM software available which I can install in my system and navigate.
Regards,
Nirmalya
Thank you I am really enjoying my lessons. Looking to expand my knowledge of SAP.
Iam employ of an government organisation from algéria wher &
how i can get more experties in hR and where
Hi ….
This Article is very good but it’s not complete . Because it skipped modules like Talent Management (TMS), Travel management , E-Recruitment, LSO
So good explanation of each classes. I would like to join SAP(HCM) online classes please provide your suggestion.