 Production Planning (PP) is a core module in SAP (both ERP and S/4HANA). As the name suggests, SAP PP is all about planning the manufacturing process. In more precise words, SAP created the PP module for supply chain planning which covers areas such as customer requirement management, production planning in a plant, requirement forecasting, quantity and capacity requirement planning, material requirement planning, and production processing. Let’s start our overview of the SAP PP module.
Production Planning (PP) is a core module in SAP (both ERP and S/4HANA). As the name suggests, SAP PP is all about planning the manufacturing process. In more precise words, SAP created the PP module for supply chain planning which covers areas such as customer requirement management, production planning in a plant, requirement forecasting, quantity and capacity requirement planning, material requirement planning, and production processing. Let’s start our overview of the SAP PP module.
SAP PP Overview
All the above-mentioned areas are categorized under the PP domain, and it is integrated with other SAP modules such as material management, sales and distribution, finance, and controlling. This interconnected network of functions and components is the building block of the SAP ERP system.
SAP PP supports three manufacturing methods:
- Discrete manufacturing
- Process manufacturing
- Repetitive manufacturing
Each of these manufacturing methods has its own process which provides unique functionalities to the respective industries. But the core concept in all the methods is based around supply chain management. Supply chain management is about the management of the flow of goods and transforming raw materials into finished products.
Master Data in PP
Master data is a vital component in the ERP. It is the base on which all the functionalities of the ERP are built upon. All modules in SAP have unique master data and when it comes to production planning, the master data are as follows:
- Material Master – material master acts as the central point for all the material-related details. From the PP perspective, basic data, MRP views, and the work scheduling view are the key areas in the material master.
- Bill of Materials – BOM consists of all the components and consumptions which are required for the manufacturing of products.
- Routing – Routing is the sequence of operations followed to produce a semi-finished good or a finished good. Routing is based on the work centers.
- Work Center – Labor, machine, or a group of machines used to perform production operations. Work centers are important for capacity planning, scheduling, and costing.
- Production Versions – Combination of a BOM and routing data which is used to uniquely identify a production method.
Supply Chain Planning
Supply chain planning and management is the core concept that is integrated throughout the PP domain. The supply chain plan is a cycle of activities that consists of:
- Sales and operations planning
- Demand management
- Long term planning
- Master production scheduling
- Material requirement planning
- Shop floor control
- Settlement
When carrying out these different activities, capacity planning and inventory management play a vital role. Capacity planning is important to handle the capacity that is available and to manage and allocate it in an optimal manner. If done accurately, this allows higher levels of productivity and better utilization of resources.
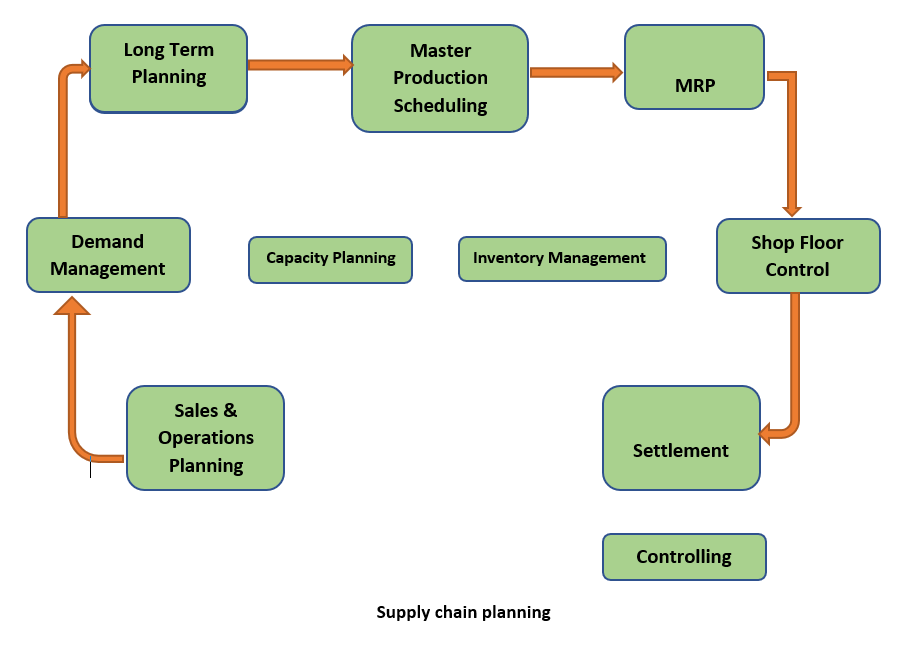
Production Planning and Control
Production planning and controlling is another important aspect covered under the PP domain and is a part of supply chain management. Production planning is mainly focused on how the demand is managed and based on the demand, how the requirement planning is done.
In SAP, demand can be entered as a planned independent requirement or as a sales order requirement. Sales order requirements can be called customer requirements because it has a direct relationship to the customer at the point of order creation. These two demands can be called the make-to-stock and make-to-order production scenarios. When the demand is entered into the system, a master production schedule can be done.
The master production schedule is used mostly to determine when the materials must be used to produce a product. The next step is the execution of MRP. The MRP determines the quantities that need to be ordered from each material in the bill of materials. This will also plan the dates on which the assemblies need to be carried out. Both planning methods can be used to effectively plan the demand.
Once MRP is executed, based on the production methods such as discrete or process manufacturing, procurement proposals will be created.
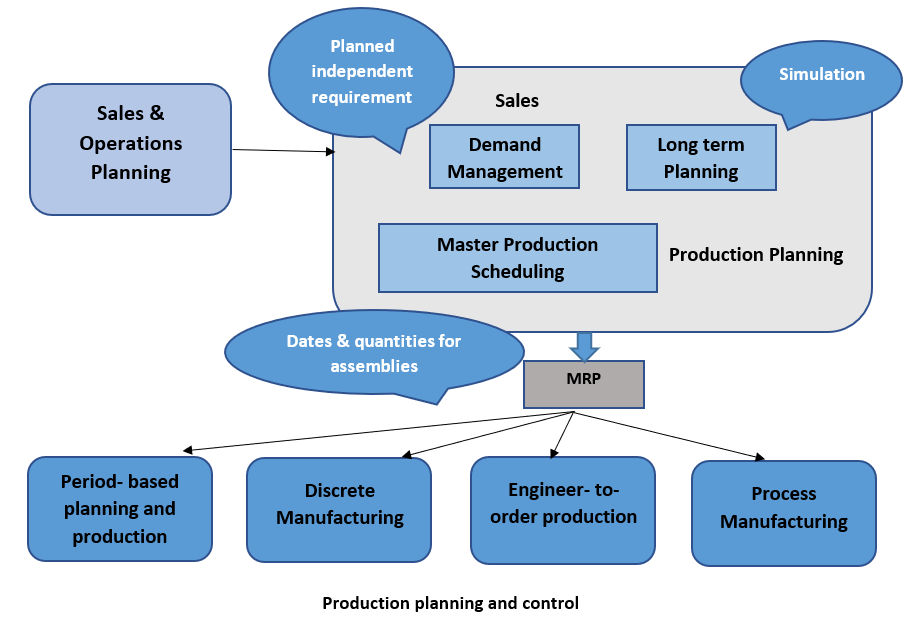
After MRP, the next activity is capacity planning and leveling. Even though MRP creates the procurement proposals, it is required to plan the capacity in an optimal manner. This allows the production run to be executed seamlessly without any floats. Capacity leveling is done to manage the capacities and ensure that capacity overloads do not occur. It can be done through work centers.
SAP Production Order
Production order is the main transactional data in the PP module. Once the MRP is executed, plan orders are created for the materials that are produced in-house. Plan orders are then converted to production orders and then released when the actual production is done.
A production order is a formal document that specifies the materials needed to be produced and in which quantities. It will have components copied from the mater data such as the components required for production copied from the BOM and the operation sequence and work centers derived from the routing.
The production order can be used to check the material availability, and actual production quantities are recorded into the production order. This is useful when calculating the actual costs of production. Most of the PP-related shop floor activities will be based on the production order.
Once the actual production is done, production order confirmations are carried out to record the actual output in the production. During the confirmation of the production order, it is possible to issue materials automatically using the backflush technique. Goods receipt can also be done automatically based on the control key settings maintained in the work center.
As mentioned earlier, actual production costs are recorded against the production order. The costs can be labor or machine-related costs. There can be multiple activity-related cost items, and these can be captured through the production order.
Once the production order is fully confirmed, order settlement and closure are done. Order settlement finalizes the costs of the order and the goods issues and goods receipt against the order. Once the order gets the TECO status, it will not be considered during the MRP run and will be removed from the stock requirement list. If there are any open reservations in the order, those will be deleted once the TECO status is set.
The closure of the production order marks the end of the supply chain planning cycle. This concludes our SAP PP Overview tutorial.
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully, it’s something we can address for you in the improvement of our free SAP PP tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to the next lesson: Production Planning Process in SAP
Go to the previous lesson: SAP for Beginners
Go to overview of the course: SAP PP Training

Thanks for the information.it is very useful
i am planning to certificate for S4P PP module. i am working more than 15 years in SAP. Please advise how it possible and how many take time.
Thank you for the effort. It is explained very well. Good luck!