 Welcome to the tutorial about SAP co-products and by-products. This tutorial is part of our SAP PP course. In this tutorial, we are going to learn what are co-products and by-products, what is the difference between them, business examples of co-products and by-products, and SAP settings relevant to them.
Welcome to the tutorial about SAP co-products and by-products. This tutorial is part of our SAP PP course. In this tutorial, we are going to learn what are co-products and by-products, what is the difference between them, business examples of co-products and by-products, and SAP settings relevant to them.
SAP Co-Product
Co-products are materials which are produced in one production process. That is, more than one final product will come out from a production process. These products will be part of the financial reporting. Any of these products will be considered as “Primary co-product” and all other products will be known as secondary co-products. Production process which gives co-products is called as “Join Production”.
SAP By-Product
By-product is an output from a production process which can be useful/sellable or sometime can be waste.
Business Example of SAP Co-Products and By-Products
Consider the Foundry Industry which manufactures castings from liquid/molten metal. Castings A and B are molded from the same mold pattern. These are intention products for this process and there are also metal wastes produced from operations like fettling and runner raiser removal process. Here, castings A and B are known as co-products and metal wastes are known as by-products.
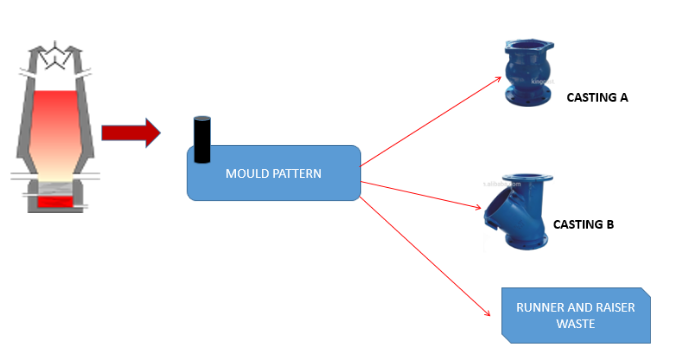
SAP Co-Product Vs By-Product
To have a better understanding of differences between co-products and by-products, let’s compare them in a table.
| SAP Co-Product | SAP By-Product | |
| Costing | Costing is based on apportionment structure defined in primary co-product. | Costing based on net realizable value. |
| BOM Settings | Co-products have negative sign along with co-product indicator in BOM. | By-products have only negative sign. |
| Financial Report | Co-products influences on financial reporting. | By-products will not have any influences on financial reporting. |
Material Master Settings
SAP co-products should have a special indicator in their material masters in MRP 2 view. In our example for materials casting A and casting B as shown on the screenshot below.
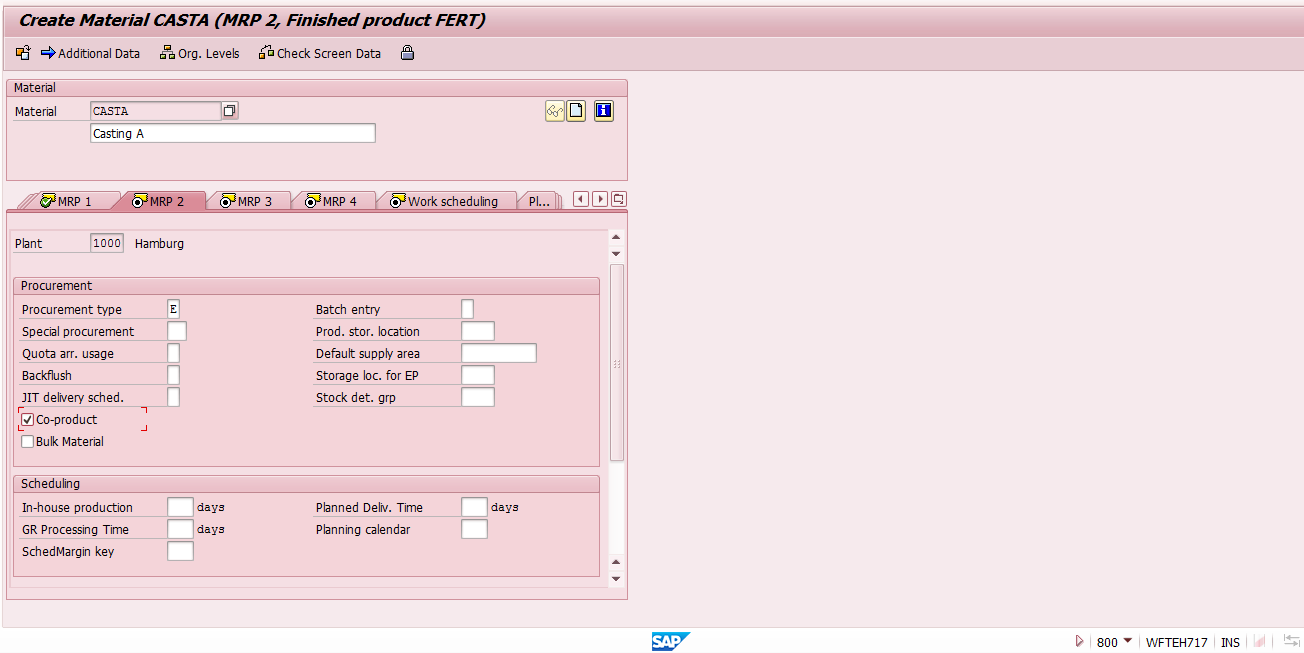
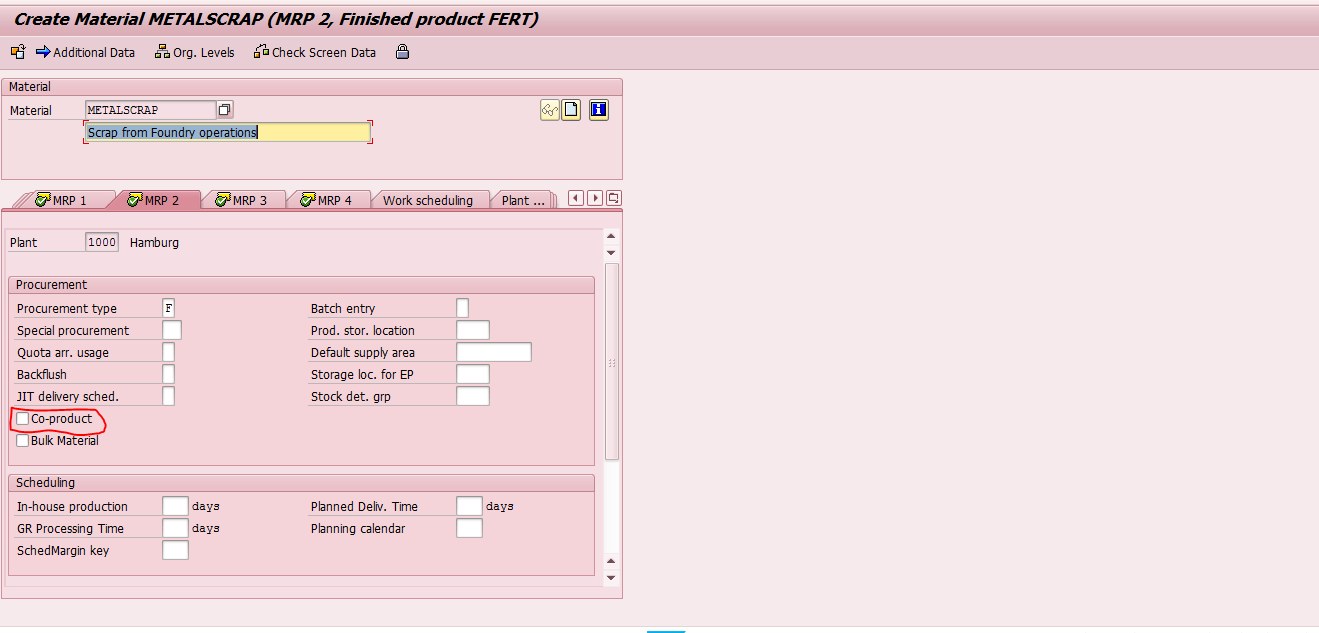
On the other hand, for the by-products this co-product indicator need not to be set.
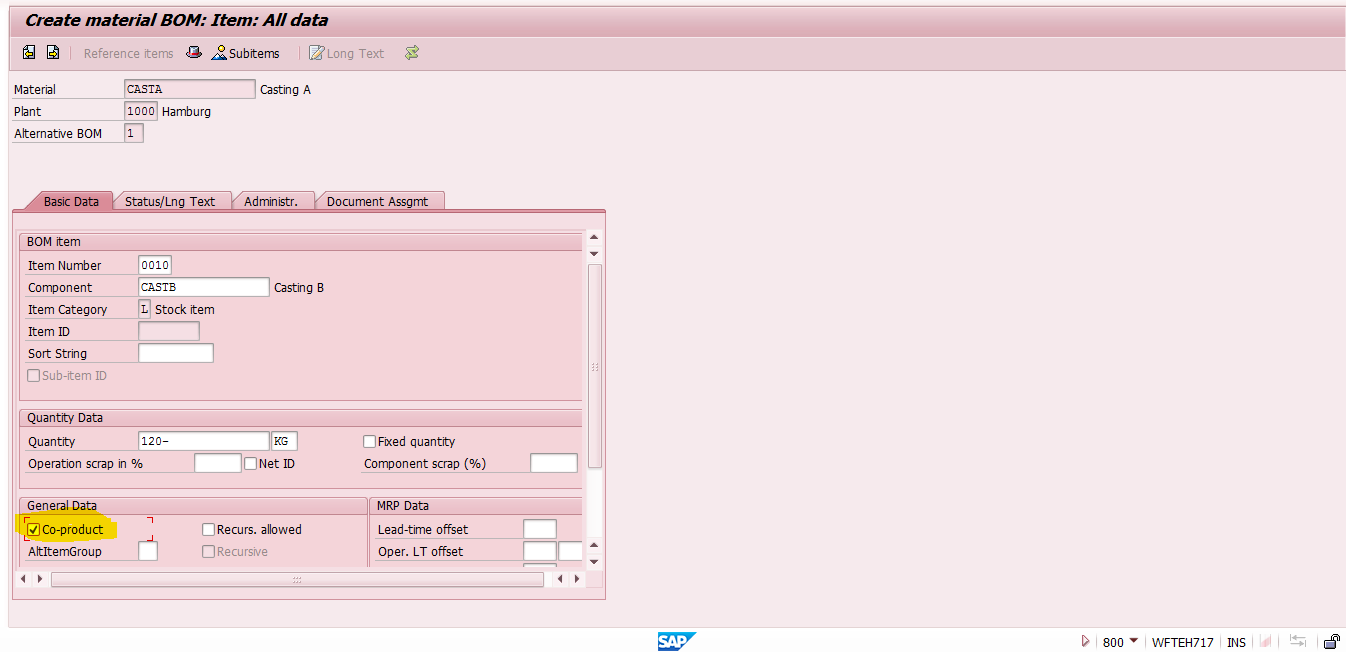
Bill of Material for Primary Co-Product
In this example, any one of the castings will be consider as a primary co-product (casting A) and another one is the secondary co-product (casting B) and bill of material (BOM) will be created for the main co-product only.
Here, the assumption is that a total of 300 KG of molten metal will be used for casting A (160 KG), casting B (120 KG) and scrap from operations (20 KG).
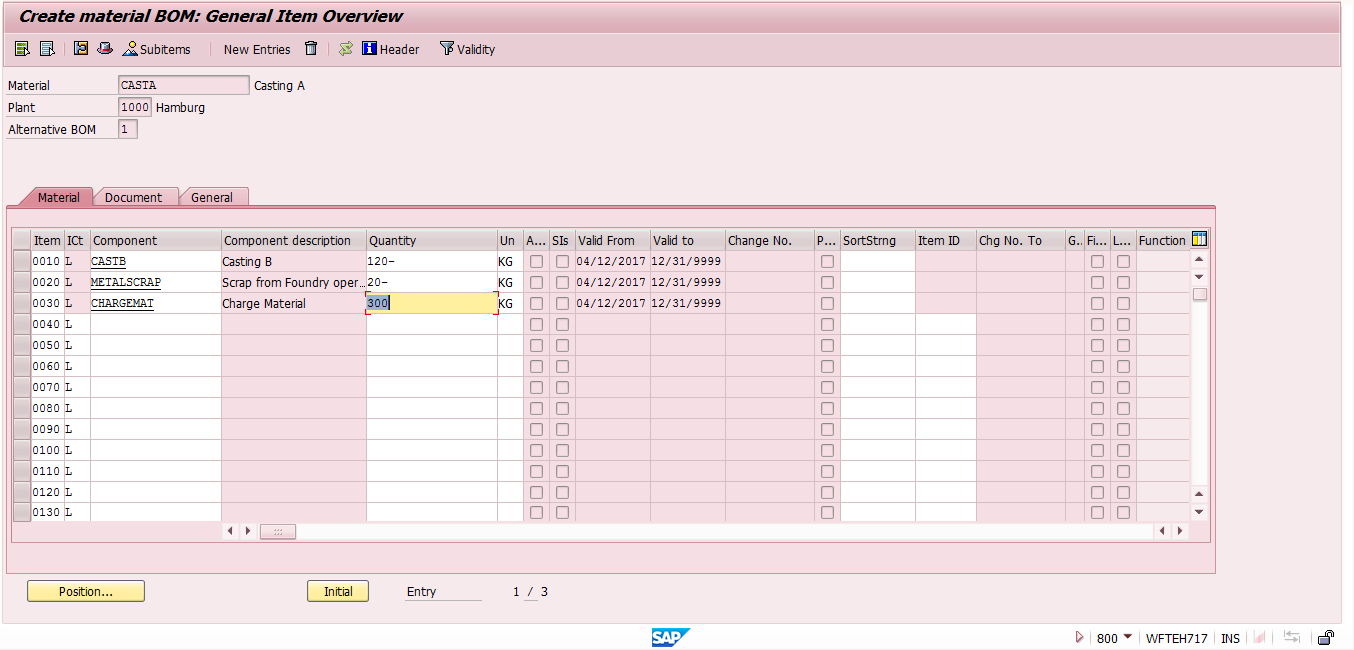
In the bill of materials, both the secondary co-product and the by-product will be maintained with a negative sign. But the secondary co-product will have “Co-product” indicator at the item level of BOM. This indicator is not required for the by-product (called METALSCRAP in our example).
Apportionment Structure and Co-Products
Co-products are costed based on apportionment structure defined in the primary co-products.
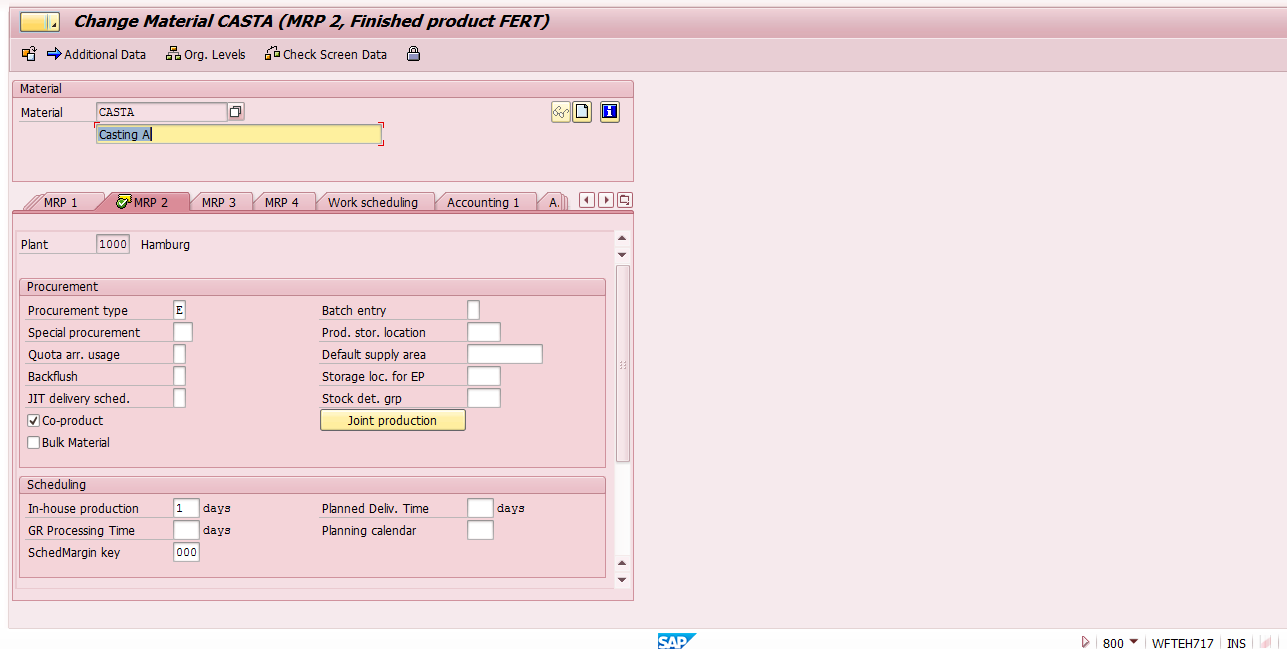
Go to master record of a co-product and click on “Join Production” button located on MRP 2 view.
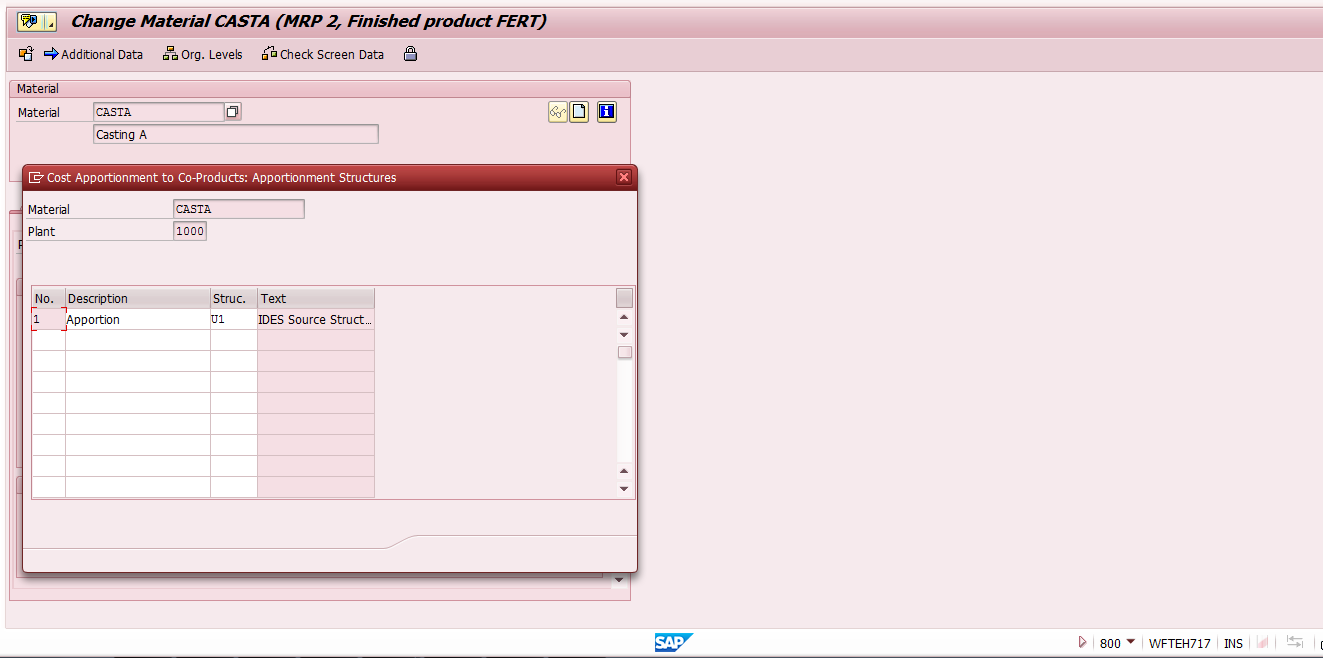
Next, assign a suitable source structure.
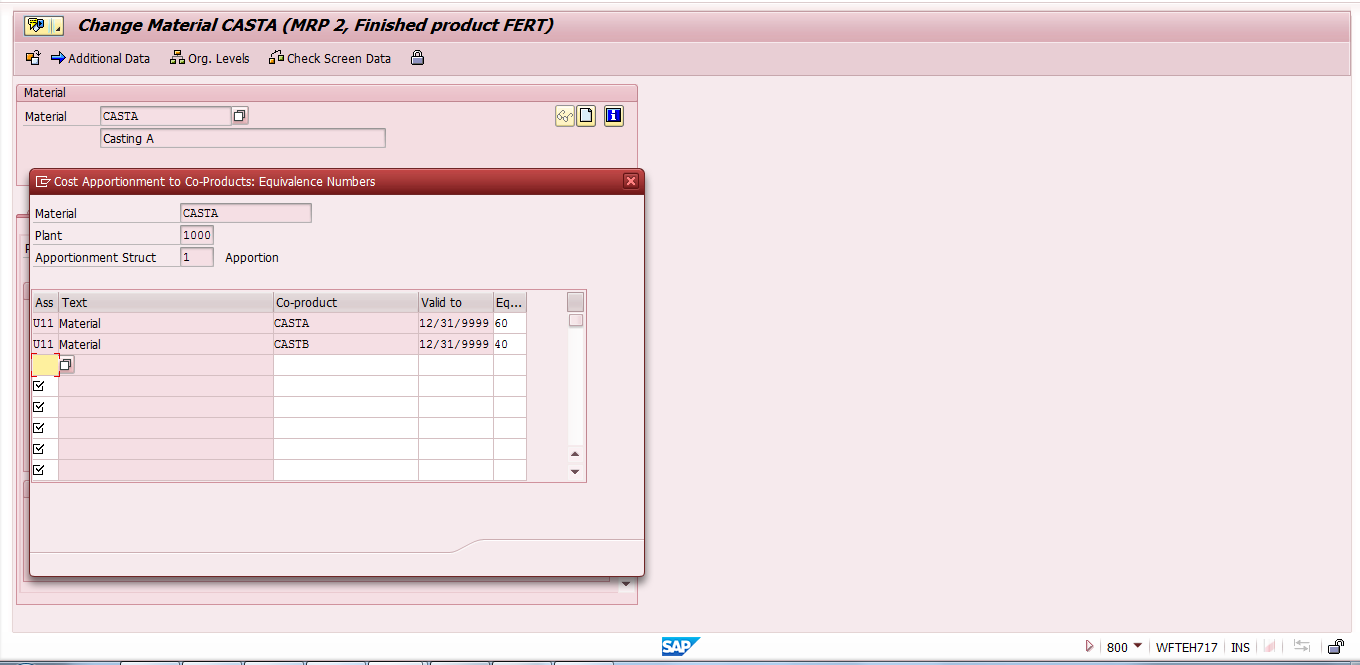
Then, enter proportion percentages or equivalence numbers for the co-products.
Example
Now, let’s discuss an example of costing for co-products using apportionment structures. The products cost consists of the following components:
Production cost = Raw material cost + Activity Cost + Overhead
In the casting example, let’s say there is not overhead cost, then
Production cost = Furnace charge material cost + Operation cost
For example, let’s say
Production cost = 12.50 + 8.50 = 21 EUR
Value for Apportion = Production cost – By-product cost
Value for Apportion = 21 – 1 = 20
Apportion for Cast A = 20 * (60 / 100) = 12 EUR
Apportion for Cast B = 20 * (40 / 100) = 8 EUR
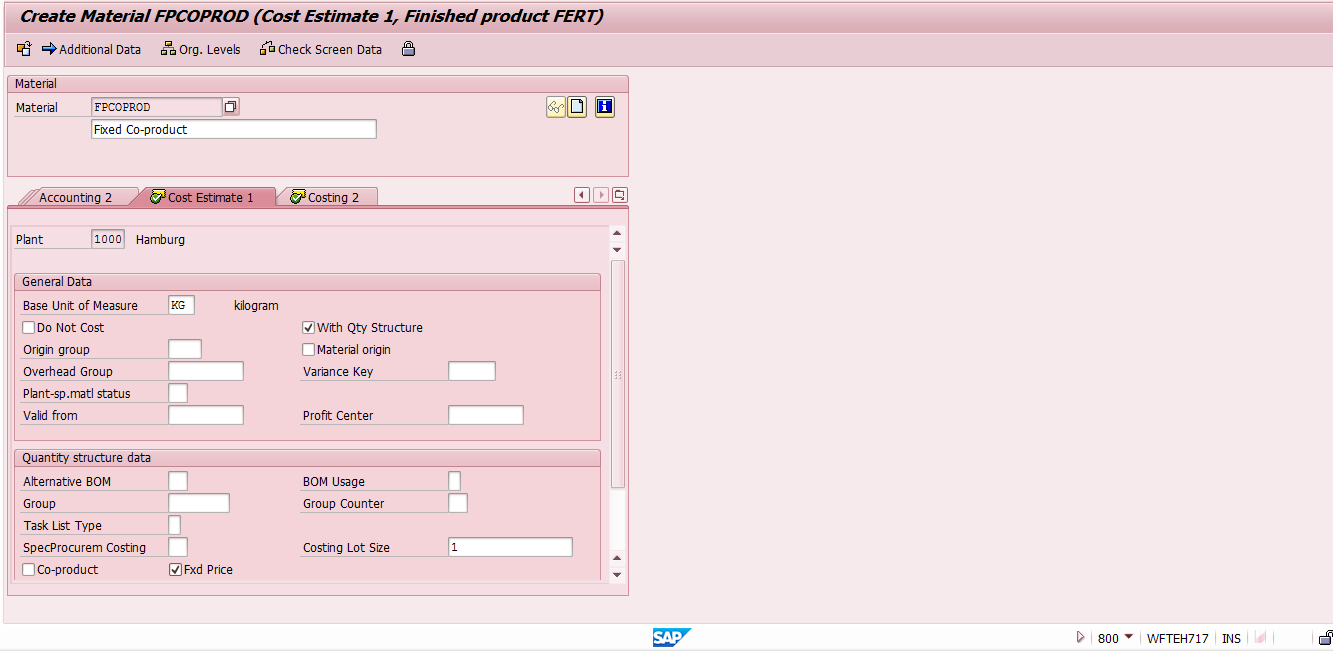
Fixed-Price Co-Product
Some of co-products for which business don’t want to do costing based on an apportionment structure can be defined as “fixed price co-products”. In SAP ERP, production cost will be subtracted from fixed price co-products and by-products and remaining value will be apportioned to the other co-products:
Value to be apportioned = Total production cost – (fixed price co-product cost + by-products total cost)
Costing of By-Products
By-products can be costed based on any one of the following method (Net Realizable Value). Price will be taken directly from the material master price. So, cost of goods manufactured (COGM) for by-products will equal to:
by-product output quantity * its price from the material master record
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP PP tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP Multiple BOM and Variant BOM
Go to previous lesson: SAP Phantom Assembly
Go to overview of the course: SAP PP Training

This is good but you may consider the posting of documents with movement type in production operation confirmation
1.by product goods issue can done via MIGO with 531 movement type
2.Co -product can post in final operation or respective operation with 101 movement type
Also in S4 HANA now we can do auto goods recept of co- product and config is matained at order type confirmation level in OPK4 N
Dear Siddheshwar,
Thanks for the additional points added. The Idea about this tutorial is to provide an overview and basic understanding of co-products and By-product at master data level. We will brief about the production order movements in upcoming tutorials. Actually co-products auto GR option was available in earlier ECC EhP6 version itself.
We really appreciate and thanks for your valuable comments.
Regards,
Velmurugan S
Hi, The above document is very nice and helpful.
Could you please, provide some document for master recipe in SAP PP-PI.
Thanks in advance.
Abhinav
Dear Experts,
I have small query currently we are doing SAP PP for Sugar Industry. For this Industry Sugar is finished product and Press mud, Bagasse and Molasses are by Products.
Ex: Cane is 10 QTL
(1) I already maintained BOM for Finished Product, Routing also maintained each operation wise duration is maintained. after that GI and GR
(2) How we maintained BOM for By products , In Routing each operation wise duration is required or not.
(3) For by products GI and GR how it will be done?
For GI which movement type and GR which movement type for by products.
For GI movement type for Raw material is 261 and for by and co-product it is 531.
if you maintain backflush indicator in material master and allow auto GI. Then system will have auto GI with 261 movement type for raw material and 531 for by as well as co-product. after production confirmation GR through MIGO will allow the GR of finished product with the movement type 101 (Unrestricted Stock) against the production order number.
Hope this will be helpful.
Thanks for the detailed step. How do you cost the Co-product B # CASTB if you dont maintain BOM & apportionment %? Does all co-product need same setting of main co-product?
Hello
Yes all co-products in BOM are costed based on apportionment structure maintained for BOM header material (i.e Main co-product ).
Regards,
Velmurugan Saravanavelu
Hello!
How is the apportionment method “Quantity based with equivalence numbers” calculated by the system????
So far I have been able to review and explain to the client calculations for:
“Quantity based” and “Equivalence numbers” but for “Quantity based with equivalence numbers” numbers dont make sense. I suspect there is an error in the calculation so I want to make sure before submitting an OS message
Any input???? THANKS!!!
Hi
thank you for your details about co-product.
And i have only one question, for the fixed price about co-product, where can we set the fixed price?
In the material master Accounting View 1?
Thank you very much.
Yes fixed price Indicator is avaialble in Costing 1 view.In this case price calculation of this co-procust will not be calculated based on cost apportionment structure
Regards,
Velmurugan S
Thanks Velmurgan ,well documented .
Very good document. Thank you for preparation and explanations.
Very helpful document
Thank you
Where I can find a report of how much co-product and by-product was produced over a period of time ?
You Can check in the SAP standard report MB52 Material documented list with Reference to Material and Movement types
Mb51
Very helpful and easily understandable…