 SAP S/4HANA is a next generation product from SAP. It is the successor of SAP R/3 and SAP ERP and runs on one of the company’s most advanced platforms – SAP HANA. SAP S/4HANA essentially changes the architecture of SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) with major impacts in several areas – including that of master data maintenance – thanks in no small part to the introduction of SAP Business Partner.
SAP S/4HANA is a next generation product from SAP. It is the successor of SAP R/3 and SAP ERP and runs on one of the company’s most advanced platforms – SAP HANA. SAP S/4HANA essentially changes the architecture of SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) with major impacts in several areas – including that of master data maintenance – thanks in no small part to the introduction of SAP Business Partner.
While SAP ECC maintains customer and vendor as separate entities, S/4HANA sees this as a redundant object model and employs a newly developed approach as part of the S/4HANA simplification list, namely, Business Partner (BP).
SAP Business Partner is not a groundbreaking concept. It has been around since the inception of SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and SAP FSCM (Financial Supply Chain Management) solutions.
SAP Business Partner Concept
The following graphic illustrates the SAP Business Partner concept and its unification object (address data).
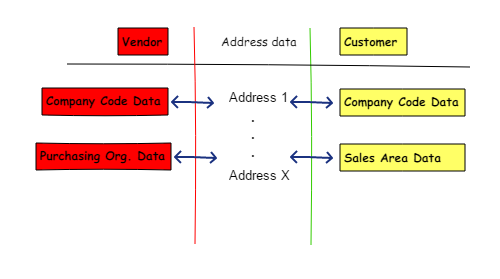
SAP ECC maintains different objects such as general data, company code data, purchasing organization data, and miscellaneous data. The maintenance of customer data requires users to also maintain general data, company code data, and sales area data.
With S/4HANA, the unification object that both customer and vendor share is address data, and thus requires new tables (e.g. table BUT000). Note that the old tables for customer data (KNA1) and vendor data (LFA1) are still available as the unique structure of company code, purchasing organization, and sales organization requires independent maintenance.
The following changes arise with the SAP Business Partner concept:
- A single unification transaction BP allows users to create, change, and display the customer and vendor. This concept supersedes old transactions that are obsolete in S/4HANA (XD01, XD02, XD03, MK01, MK02, MK03, etc.).
- Unification of the address data/object allows both customer and vendor to use the same screen/data set.
- Users can maintain a new Business Partner as both customer and vendor.
The SAP Business Partner concept impacts are as follows:
- LSMW or customized upload tools from a previous SAP ECC environment will no longer function.
- Data migration to comply with the HANA platform. Steps include preparation, synchronization, conversion processes, and post processing. If you are a member of a data migration team, you may wish to refer to and download the OSS notes (2265093) for more information.
- Data cleansing is necessary to align the address format, VAT, and several other attributes. This is particularly relevant if the Business Partner acts as both customer and vendor.
- A new business process flow is necessary to maintain the Business Partner. In the past two separate teams may have been used to maintain customer and vendor data. However, as the data is now linked and the same screen used, a new policy should be standardized.
- The old customized program from ECC will not be compatible to read the master data. Consider updating those transactions, especially transactions using BAPI.
SAP SD Business Partner in Action
- First, let’s try to call a standard transaction XD01 to create a new customer. The system will raise a message that the transaction is obsolete before redirecting to transaction BP.
- Now call the correct transaction BP and select the Organization.
- Business Partner (BP) role will play an important part upon creation because each role will carry a different object. In Sales and Distribution, there are two standard roles you can utilize:
- FLCU00 – FI Customer for Company Code data
- FLCU01 – SD Customer for Sales Organization data. For this example we will use the combination roles of Company Code data and Sales data which were configured prior to this transaction.
- Select the role.
Assign a number range to the newly created customer by selecting the grouping. - In the Address tab, enter the mandatory field (which is set in the configuration). Then select the tab Address Overview.
- You may enter different general attributes by clicking on the various tabs alongside the Address Overview tab. When complete, click on the Company Code button at the top of the screen.
- The important fields here are Company Code and Reconciliation Account. Like general data, you may enter other information such as Payment Method or Dunning Procedure in their respective tabs.
- Click on the Sales and Distribution button and enter the sales area. Most of the fields here are similar to the ECC version.
- Enter the necessary information in the required fields from Tab Sales to Partner Function then click on the save button. You will see a new customer number assigned (assuming the auto number range was previously configured).
- Under the Partner Function tab you will notice that the Number field entry is identical to that of the Business Partner field.
SAP Business Partner Configuration
Now we can look at how to combine several roles into new BP Roles Categories that incorporate the Company Code View and the Sales Organizational View.
- To begin with, we need to define BP Roles Categories. In order to do so, navigate the following customization path: SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Business Partner Roles -> Define BP Roles.
- Double click on BP Roles Categories and then select the New Entries button. Define the key for your new category and enter the description. Select 0 (general data) in the Differentiation Type and check all potential business partner categories. Click the Save button.
- Next, navigate the following customization path: SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Business Partner Roles -> Define BP Role Groupings.
- Double click on the BP Role Grouping Categories and create new entries. Now repeat the same steps taken with the BP Role Grouping and create a new entry before adding the title and description. After that, assign the role group you created previously.
- Double click on the sub-folder BP Role Groupings -> BP Roles. Click on New Entries and enter the BP Roles (FLCU00 and FLCU01). Click Save.
- Follow this customization path: SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Number Ranges and Groupings -> Define Number Ranges.
- Then create new number ranges that will be assigned to our customized BP roles.
- Select SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Number Ranges and Groupings -> Define Groupings and Assign Number Ranges.
- Create a new entry for the grouping and then enter the short and long description along with the appropriate number range. Use the Internal Standard Grouping radio button to determine the default number range if the grouping was not entered during Business Partner creation.
- To make the Partner Functions share the same number as Business Partner, simply select the following customization path: SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Master Data Synchronization -> Customer/Vendor Integration -> Business Partner Settings -> Field Assignment for Customer Integration -> Assign Keys -> Define Number Assignment for Direction BP to Customer.
- Assign the Grouping BP to the existing account group from SD, then click on the relevant number indicator. The number range for Customer (t-code OVZC) should be the same as the BP number range. Check the box under the External column.
Common Questions
1. How do I generate an SAP Business Partner with the roles of Customer and Vendor at the same time?
Run the transaction to create a new BP Role Grouping, then assign the standard BP Role for Vendor and Customer. Additionally, create a new grouping and assign a dedicated number range (if internal).
2. I created a sales employee from transaction VPE1. Why is the system unable to recognize the personnel number when I try to assign it in Partner Function? Does it have anything to do with the BP concept?
In our experience with SAP S/4HANA, yes. Please check the notes below for more information:
The directions contained in the above notes helped to resolve the issue. The assignment process proceeded without issue when the personnel number was recognized.
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP SD tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP Partner Function Configuration
Go to previous lesson: SAP Sales Information System
Go to overview of the course: SAP SD Training

It would have been better, if screen shots are added to clearly show all the partner functions being configured in customer master
How do you prevent a vendor being created when you create a Business partner. The business partner is created for vendor that already exists
If Vendor is already created then system won’t create it again. Only updates will be done.